
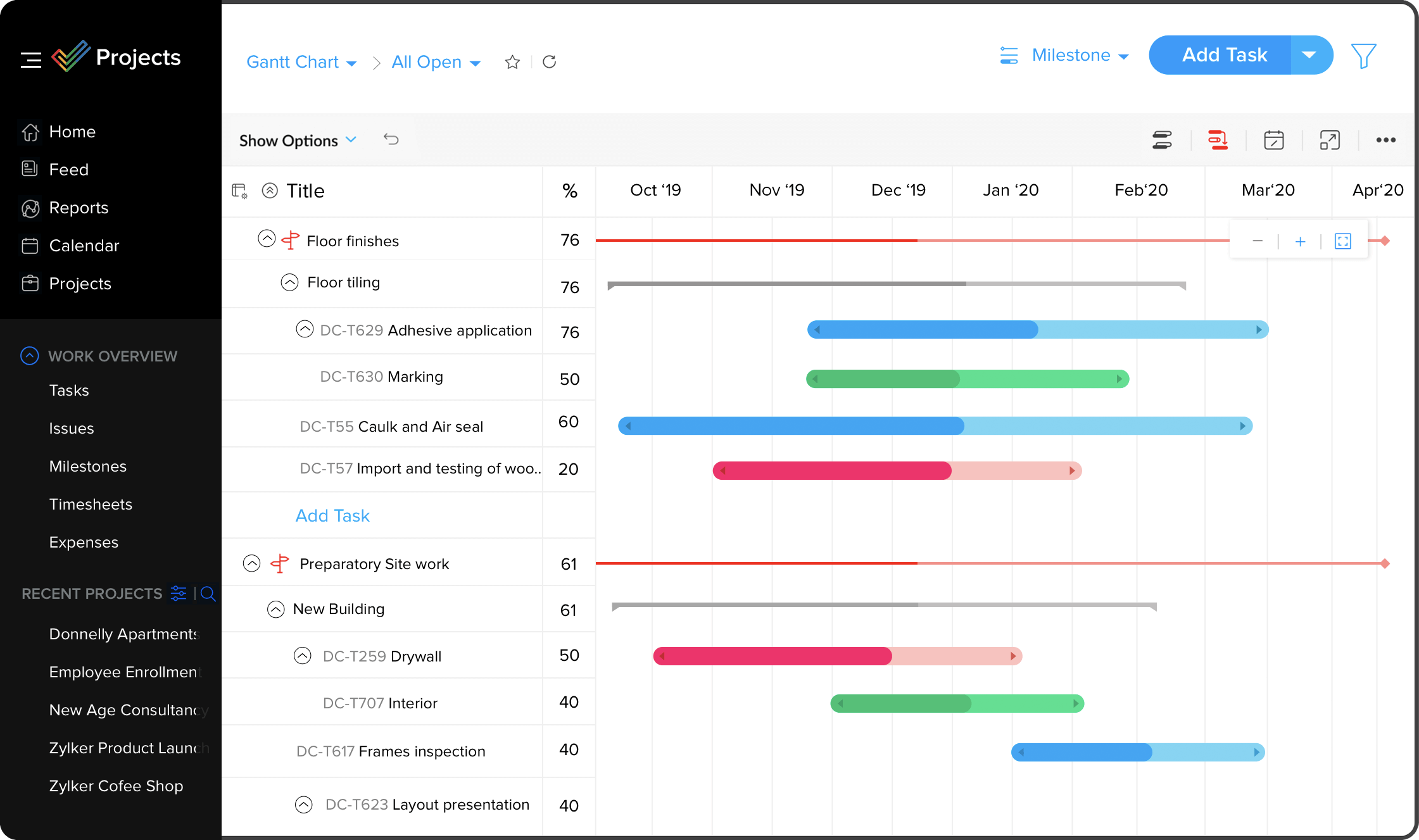
The potential causes of the failure are then listed beneath the first failure. For root cause analysis, the failure under investigation should be listed on top of the tree diagram. Tree diagrams use a structure with broader categories on top and break them down into details at the lower levels (Liu, 2013). The group then takes the brainstormed list and organizes the potential reasons using an interrelationship diagram (Source: )Įdit this Diagram What is a Tree Diagram? The office manager of the group conducts a brainstorming session to generate potential reasons for the lack of effective and timely follow-up calls. In particular, the patients are frustrated that the promised call notifying them of the test results is either delayed or must be initiated by the patient.
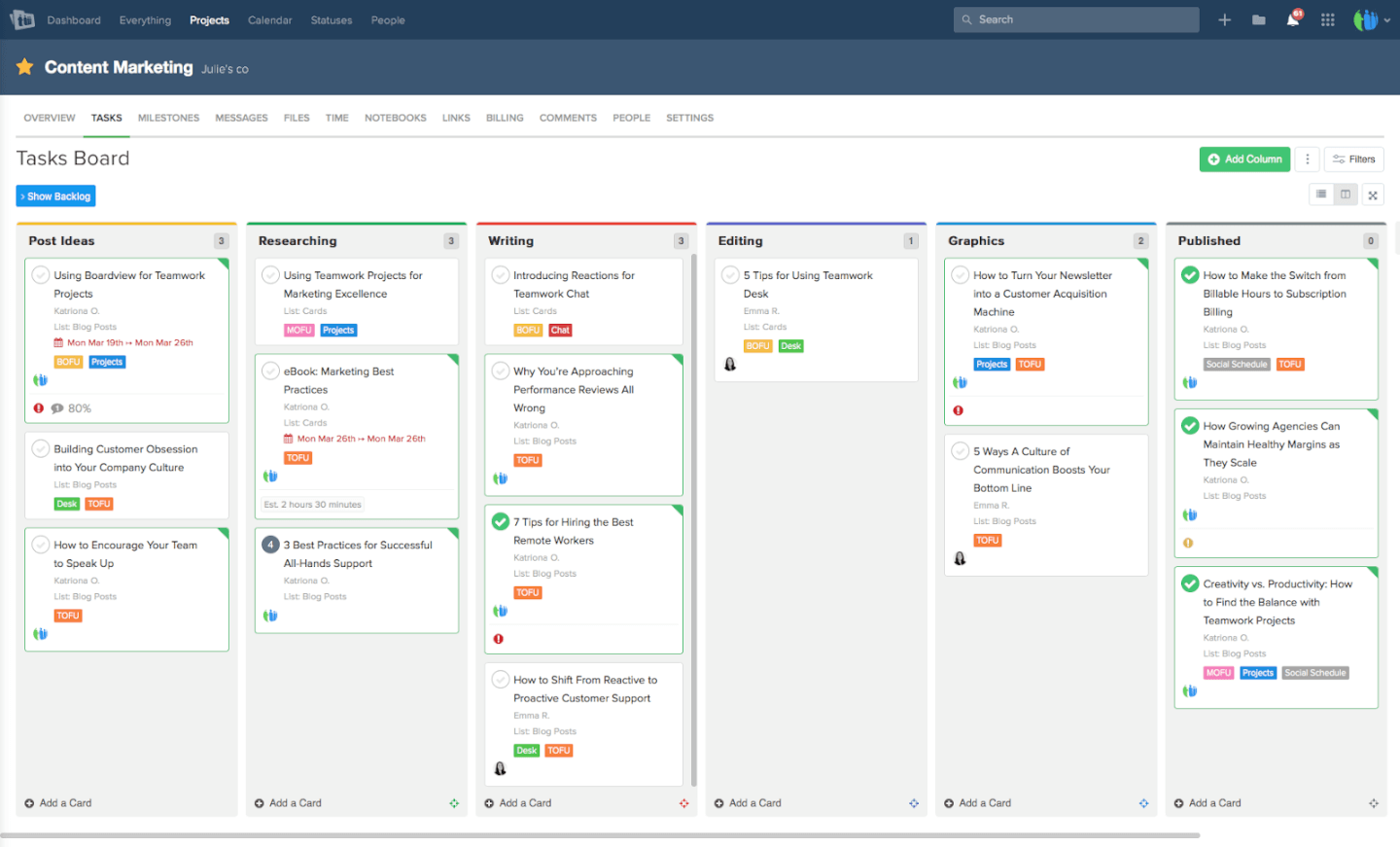
Interrelationship Diagram ExampleĪ local physicians’ group is experiencing a relatively high number of patient complaints regarding the lack of returned phone calls following a patient visit where some kind of test was ordered. Arrows are used to show the direction of influences, and one item may influence many other items or be influenced by many other items. Interrelationship diagrams use arrows to show relationships, such as the inputs, outputs, and interconnections among processes (Dias and Saraiva, 2004). Interrelationship Diagram is an analysis tool that helps you discover the cause and effect among critical issues.
Label: labeling each group of cards into categories and eliminate duplicate ideas.Īffinity Diagram Example – Sustainability ChangeĬonduct a brainstorming session and use the affinity diagram to identify how to successfully implement and sustain change within an organization as shown in the Figure below:Įdit this Diagram What is an Interrelationship Diagram?. Group: Look for ideas that seem to be related in some way and place them side by side. Capture: Record each idea with a marking pen on a separate sticky note or card. The affinity diagram is normally led by a facilitator to guide the team through the following steps: To creating an affinity diagram, it involves: collect/organized and analyzed data into useful information. It was created in the 1960s by Japanese anthropologist Jiro Kawakita. This idea creation method taps a team’s creativity and intuition. After generating ideas, group them according to their affinity, or similarity. It is used to generate, organize, and consolidate information related to a product, process, complex issue, or problem. The affinity diagram organizes a large number of ideas into their natural relationships. The Most Essential 7 management and planning tools What is an Affinity Diagram? Process decision tree: Systematically identifies what might go wrong in a plan under development. Arrow diagram: Shows the required order of tasks in a project or process, the best schedule for the entire project, and potential scheduling and resource problems and their solutions. A prioritization matrix is an L-shaped matrix that uses pairwise comparisons of a list of options to a set of criteria to choose the best option(s). Matrix data analysis: A complex mathematical technique for analyzing matrices, often replaced by a similar prioritization matrix. L Shaped Matrix diagram: Shows the relationship between two, three, or four groups of information and can give information about the relationship, such as its strength, the roles played by various individuals, or measurements. Tree diagram: Breaks down broad categories into finer and finer levels of detail, helping to move step-by-step thinking from generalities to specifics. Interrelationship diagram: Shows cause-and-effect relationships and helps analyze the natural links between different aspects of a complex situation. Affinity diagram Organizes a large number of ideas into their natural relationships. These 7 Management and Planning tools are: However, they were assembled as a set of techniques for achieving efficiencies in the planning and management of operations. 
These tools were developed independently for diverse purposes. This toolset can be used to encourage innovation, facilitate communication, and help for planning in a team approach.

The seven management and planning tools were the result of operations research and TQM in Japan after World War II in the 1970s.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
